
How to Optimize Your Content for Featured Snippets
- 06 Oct, 2025
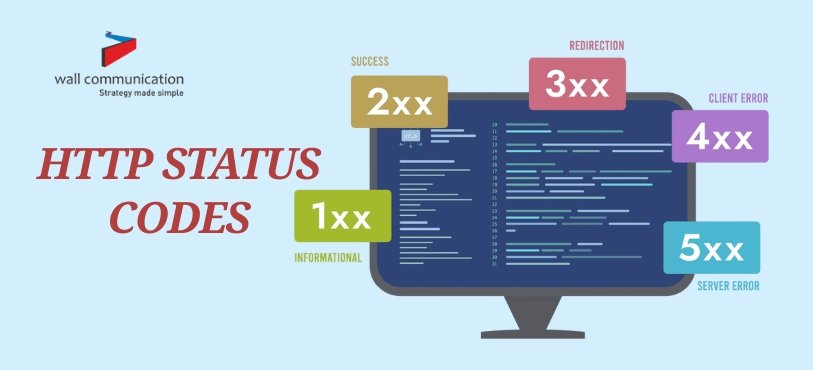
When you use the internet, it might often feel like you're lost in a maze of digital communication. HTTP status codes are an important tool that helps both consumers and developers navigate the web. These codes are important for knowing how a client, such as a web browser, and a server talk to each other. In this blog, we will provide the full explanation about HTTP status codes, including what they are, why they matter, and a full list to help you understand them better.
By the end of the blog, you will be aware of what HTTP Status Codes are.
Servers send back three-digit HTTP status codes in response to a client's request to that server. These codes are part of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and let users and developers know what happened with their requests on the web.
HTTP status codes have three digits and a brief description. Understanding this pattern helps users easily identify response types. The first code digit specifies the response's broad category:
Informational Replies
Digital marketers, web developers, and casual internet users need HTTP status codes. The reason:
User Experience: HTTP status codes greatly affect user experience. Understanding these codes can assist in discovering website performance issues. For instance, 404 Not Found errors can annoy users and raise bounce rates.
Implications of SEO: HTTP status codes affect webpage rankings on Google. Many error codes, especially 404 and 500 errors, might hurt your site's SEO, so they must be managed.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting: HTTP status codes aid troubleshooting. Developers may quickly discover and fix issues by monitoring these codes, improving user experience and website reliability.
Five kinds of HTTP status codes reflect different responses. A thorough analysis of these categories as a list of HTTP codes is below.
1xx: Informational Responses
Informational answers show the server is processing the request. These codes are crucial for client-server communication but are rarely viewed by end-users.
100 Continue: The client should continue with the request.
101 Switching Protocols: The server is switching protocols as requested by the client.
102 Processing: The server is processing the request, but no response is available yet (used in WebDAV).
2xx: Success Codes
Success codes indicate the request was received, understood, and accepted. This category is essential for verifying interactions.
200 OK: The request has succeeded, and the server is returning the requested data.
201 Created: A new resource has been successfully created in response to the request.
202 Accepted: The request has been accepted for processing, but the processing is not yet complete.
204 No Content: The server successfully processed the request, but there’s no content to return.
3xx: Redirections
Redirection codes require additional action to complete requests. These redirect URLs help users find their way.
300 Multiple Choice: The request has multiple possible responses, and the user can select one.
301 Moved Permanently: The requested resource has been permanently moved to a new URL.
302 Found: The resource is temporarily located at a different URL.
303 See Other: The response to the request can be found at another URL, using the GET method.
304 Not Modified: The resource has not been modified since the last request.
4xx: Client Error Codes
Client error codes reflect incorrect grammar or unfulfilled requests. These codes are essential for user error analysis.
400 Bad Request: The server cannot process the request due to a client error.
401 Unauthorised: Authentication is required, and the request has not been applied.
403 Forbidden: The server understands the request but refuses to authorise it.
404 Not Found: The requested resource could not be found on the server.
405 Method Not Allowed: The request method is not supported for the requested resource.
5xx: Server Errors
Server error codes mean the server failed to process a request. Understanding server-side issues requires this code.
500 Internal Server Error: A generic error message when the server encounters an unexpected condition.
501 Not Implemented: The server does not support the functionality required to fulfil the request.
502 Bad Gateway: The server received an invalid response from the upstream server.
503 Service Unavailable: The server is currently unable to handle the request due to temporary overload or maintenance.
504 Gateway Timeout: The server did not receive a timely response from the upstream server.
Improve User Experience
Web user experience depends on HTTP status codes. So how:
Clear Communication: Users get immediate request responses. For instance, a 200 OK response means a page loaded correctly, but a 404 Not Found error means the website is unavailable.
User Guidance: Users can avoid frustration and confusion by using redirection codes like 301 Moved Permanently.
SEO Importance
Digital marketers must understand HTTP status codes for SEO. The reason:
Crawling: Search engines index websites by crawling. High 404 errors can slow this procedure and lower your site's search rankings.
User Engagement: Smooth user experiences increase engagement and decrease bounce rates. Search engines favour user-friendly sites.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Monitoring HTTP status codes aids troubleshooting:
Identifying faults: Checking error codes often can reveal broken links or server faults.
Improving Site Performance: Fixing errors and improving code can boost website performance and user experience.
HTTP Status Code 404: Not Found
HTTP status code 404 Not Found is well-known. This value means the server cannot find the resource. User frustration from 404 errors might raise bounce rates and lost conversions.
Causes of 404 Errors
There are various causes of 404 errors:
Incorrect URL: Users may have typed it wrong.
Broken Links: 404 errors might result from broken links to deleted or relocated pages.
Outdated Bookmarks: Users may be accessing a dead page.
How to Handle 404 Errors
Consider these 404 error mitigation strategies:
Custom 404 Pages: Make user-friendly 404 pages to redirect visitors to appropriate site content. This can enhance user retention and lower bounce rates.
301 redirect: To route users to a moved page, use a 301 redirect.
Regular Audits: Audit your website often to find and fix broken links.
HTTP Status Code 500: Internal Server Error
Another typical server problem HTTP status code is 500 Internal Server Error. Troubleshooting is difficult without particular problem specifics.
Causes of 500 Errors
Server Configuration Issues: Misconfigurations in server settings can cause this issue.
Coding mistakes: Website coding bugs can cause 500 errors.
Server Overload: High traffic can cause server failure.
How to Fix 500 Errors
Web developers can fix 500 errors:
Check Server Logs: Refer to server logs to determine the error's cause.
Debug Code: Test and debug website code to detect bugs.
Optimisation: Make sure the server can handle traffic and is correctly set up.
Informational Responses (1xx)
Informational answers show the server is processing the request. These codes are crucial for client-server communication but are rarely viewed by end-users.
100 Continue: The client should continue the request.
101 Switching Protocols: The server switches protocols per client request.
Success Codes (2xx)
Success codes indicate the request was received, understood, and accepted. This category is essential for verifying interactions.
200 OK: Request successful.
201 Created: A new resource was created.
202 Accepted: The request has been accepted for processing, but it is not yet complete.
Redirection Codes (3xx)
Redirection codes require additional action to complete requests. These redirect URLs help users find their way.
301 Moved Permanently: The requested resource has been permanently relocated to a new URL.
302 Found: Resource is temporarily at another URL.
4xx Client Error Codes
Client error codes reflect incorrect grammar or unfulfilled requests. These codes are essential for user error analysis.
400 Bad Request: Client fault prevents server processing.
401 Unauthorised: Request has not been authenticated.
Server Error Codes (5xx)
These codes indicate a server failure to fulfil a valid request. Understanding server-side issues requires this code.
500 Internal Server Error: A generic server error message.
503 Service Down: The server is overloaded or under maintenance and cannot process the request.
Best Practices for HTTP Status Code Management
Monitor Regularly: Regularly examine your website's HTTP status codes. Google Analytics or server logs can track performance and discover faults.
Use Redirects Smartly: Use 301 redirects to route users to new pages when relocating or removing them. This maintains SEO and user experience.
Make Custom Error Pages: Customise error pages with useful information and navigation. This reduces error frustration and keeps users engaged with your site.
Conduct Regular Audits: Audit your website regularly for broken links and error codes. This can be automated with Screaming Frog or Sitebulb.
Improve Server Performance: Optimise your server for traffic. Check server configurations and upgrade as needed.
Digital marketers and site developers must understand HTTP status codes. These codes represent request status and display website performance. By understanding HTTP status codes and their effects, you can improve your website's search engine rankings with the best digital marketing agency. Monitoring and managing HTTP status codes improve SEO, user engagement, and conversion rates. Keep these codes in mind as you explore the digital world to make your website user-friendly and efficient. Mastering HTTP status codes will help marketers, developers, and curious users improve online experiences. You can create a website to satisfy user needs and meet digital marketing goals by following best practices and monitoring HTTP status codes. Your website's performance and user satisfaction are code away.
With this, we hope you got the answers to all your queries regarding HTTP codes.